Over time saving and adding files to your hard drive can take up disk space, especially when you copied or saved the same files to other folder locations. Windows does have the Disk Cleanup tool to help delete files found in temp folders and other locations, but it does not include functionality for finding duplicate files in Windows or provide any built in tools.
Windows XP Service Pack 2 Support Tools, which is a separate download, does include a duplicate finder utility, but it lacks functionality. Instead, I like to use a third party freeware tool called Duplicate File Finder that allows for filtering and better control when searching for duplicate files.
Once you have downloaded and installed Duplicate File Finder start the program by clicking on Duplicate File Finder either from the Program group location it was installed, or from the Desktop shortcut (if you selected to have it created during setup).

In the left window pane, you can expand the drives to select individual folders or click on the drive itself to select all folders. You can also leave the two boxes checked under Folder Options:.
Three areas that you may want to change options are the File Comparison Method, Advanced Options and File Filter options.
For File Comparison Method, you can choose to have Duplicate File Finder compare files by name, content, size, or a combination of both. When selecting the combination Name and Size or Contents and Name, scanning for duplicate files will take longer.
The File Filter allows you to select the type(s) of file to search. Select which files you want by checking the check box in the select Filter column. You list of selected file types will display in the bar below File Filter:
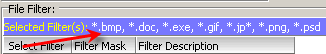
You can also add file type to the filter by selecting the New Filter button, then selecting it in the list after it has been created.
The last option you want to configure is the Advanced Options Exclude Folders:
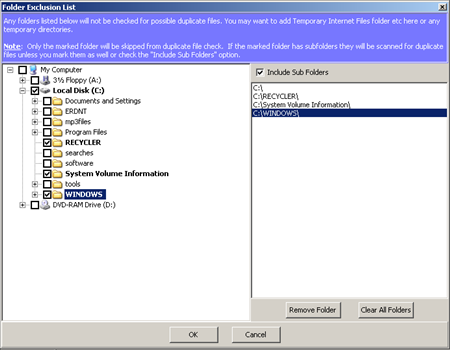
Here you should select any folders that should be skipped from scanning. By default, the Recycler, System Volume Information and Windows folders will not be scanned. Also notice that just the folder that is selected will skipped, unless you also check subfolders or you leave the Include Sub Folders checked (right side above the display of selected folders).
When you have finished selecting options, start the scan by clicking the Start Search button below the File Filter list. You can view the progress or abort the search.

After completing the scan (CRC checking), the results window will display, listing the duplicate files found, and the various options to choose from.

Here you can expand the list and either select all or some files to delete. The toolbar options include save the search results, select or unselect marked files, expand and collapse the tree view, move the file to a different folder and delete marked files.
One feature that makes Duplicate File Finder shine is the capability to right click on a file and open a command prompt to the directory of the selected file, open the target folder via Windows Explorer, copy to clipboard, execute the file, or select properties of the file.
After carefully verifying the list, you can delete any duplicate files Recycle bin (trash can) icon in the toolbar. An important note about deleting, the files are only soft deleted, meaning they will remain in the Recycle bin until you empty it. This option allows you to delay permanently deleting the files in the event you made a mistake and need to restore the duplicate file later.
Duplicate File Finder is a great tool and it's free. unfortuanately there is no current support as of this writing. Supported version of Windows are 98/NT/2k/Me/XP/95/2003. I have also been able to use it on Windows Vista.
NOTE: You are responsible to verify any files you select for deletion and has been verified it is no longer needed. Always exclude System folders from being scanned and never delete any System file or file that you can not 100% percent identify. It's best to leave the file on your hard drive instead of deleting. Always create a backup and restore point before proceeding.








